How Search Intent Modifiers Affect Google SERP Features
Did you know that just one or two extra words in a search query can affect the type or types of SERP features Google shows in its results?
In the world of SEO, we call these one or two extra words ‘search intent modifiers’. Why are we bothered with just one or two extra words? Because they can make or break you in SERP rankings.
Back in its early infancy, every website page listed on Google’s result pages looked pretty much the same. Title, a rough snippet of text, a URL. It didn’t tell you too much – you just had to click to find out what was on the page. This is no longer the case.
In its ongoing quest to make daily life ever-easier for Internet users, Google has steadily been adding more and more user-friendly features to its results pages. These are what we now call SERP features.
By reading this article you will learn:
- Magic modifier words to use on your website
- Google’s main SERP features circa 2021 and which can apply to your website
- How search intent and search intent modifiers can trigger specific SERP features
- How to optimize your content for both search intent and specific SERP features
Our goal is that you will have a better understanding of the current Google SERP landscape, become aware of the opportunities you have to capture more Google SERP real estate, and experience the thrill of seeing your website presented in fresh ways to your searchers.
In This Article
What is a Google SERP?
A Google SERP is a search (S) engine (E) results (R) page (P). When you type a query or search term into the Google search bar, Google returns hundreds of thousands or even millions of results in the form of links to individual websites (or specific pages on those websites). These results are usually limited to 10 per search engine results page, and can run to hundreds of pages. (Remember though, that anything after Page 1 of the SERPs is rarely seen by the searcher.)
Where once these SERPs were simplistic, featuring a couple of lines showing title, description and URL, today SERPs show you a variety of content options, including organic listings, rich snippets, paid ads, related content, and more.
What are SERP Features?
SERP features are additional, special content elements you see on SERPs that serve to give you even more answers to your search query.
All those pluses are your SERP features: any result on the Google SERP that is not a traditional organic link. These SERP features are intended to offer users maximum information with minimum effort. (Some require not so much as a click – the information is all right there on the SERP!)
Popular Google SERP Features that Matter to Businesses
Here is an extensive list of current Google SERP features as of the time of writing. As you read and look at the screenshots keep in mind that Google is always adjusting how it displays SERP features and updating the type of SERP features used.
How can you take advantage of some, or even all, of these features to increase your visibility, ranking, authority, and, ultimately, sales?
1. Featured Snippet
The Featured Snippet is designed to give a summarized answer to a specific question typed into the Google search bar. It is one of the most prominent SERP features, always appearing in the very first position on SERPs, i.e., above all other features, including organic search results, but underneath paid ads – money always talks first.
Featured snippets are presented in any one of a number of formats, including paragraphs, bulleted lists, numbered lists, tables, and even video.
2. Local Pack
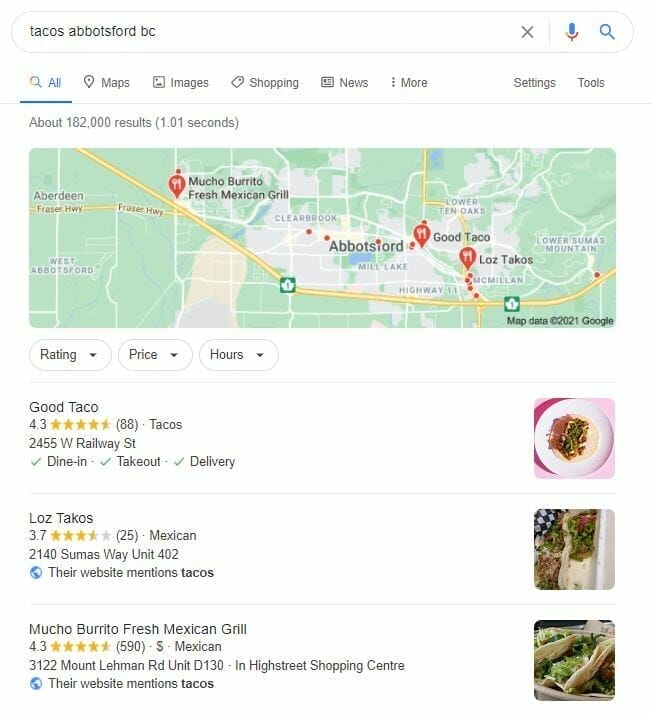
The Local Pack shows location-based results based on what your query is (subject) and where you are (geography).
These pop up in answer to questions posed on Google like “massage therapist near me?, “best coffee in Vancouver?, “closest pizza Times Square? etc. As such, optimizing for the Local Pack is particularly important for local business success.
Generally, a Local Pack shows up in response to a geographically-based query as a map at the top of SERPs (but again, below any paid ads) with pins indicating the business’ location and the top three search results (in the Google equivalent of the Olympics podium).
3. Instant Answer
The Instant Answer feature appears up when Google can find a quick and easy immediate answer – no click-through required – to a specific search query. These answers are sourced from Google’s Knowledge Graph.
3. Knowledge Graph
The Knowledge Graph shows up on the right-hand side of a SERP, and is served in response to searches for specific people or organizations. The Knowledge Graph will display factual information – what, where, when, how, location, open hours, contact details, images of said person/organization, as well as anything else Google thinks useful to the searcher.
Google sources all the Knowledge Graph information from both Google data and external sources. This differs from the Knowledge Panel, where information is sourced from only Google data.
4. Knowledge Panel
The Knowledge Panel, like the Knowledge Graph mostly served up on the right side of the SERP, provides background knowledge about a topic. For example, this is a common SERP feature for queries related to a famous person, place, thing, brand etc. These are nearly identical to Knowledge Graphs, except that Google pulls information only from Google My Business Listings or Google Maps.
5. People Also Ask (PAA)
People Also Ask pops up as a series of additional questions in boxes just beneath your original query. These questions are closely related to the original search query typed into the search bar and at times it’s humorous to see what people also search for (and also very informative for business owners to see what customers are searching for).
6. Reviews
Reviews show up as orange star ratings in ordinary organic snippets, the local pack, and various other places. They will appear under your website result in SERPs if your business has received Google reviews directly from Internet users. It can appear for any type of a query if the result has reviewable content and the right schema markup.
This is one SERP feature you want to take advantage of: Reviews in SERPs really matter.
Search results with reviews have a higher average CTR because they convey user trust in your offering. Which translates to Google trust in your authority. Which translates to better rankings.
Unsure about reviews? Read our stance on the importance of reviews for SEO and overall business success.
7. Sitelinks
Sitelinks show up immediately below the organic search result which pops up for your site (Title, Meta Description and URL) – but only if they are worthwhile! If Google deems it valuable to the user and aligned with the user’s search intent, they will offer these additional sitelinks, directing users to related areas and pages of your website.
8. Images
Image results appear for any search queries judged by Google to warrant visual aids (be they photographs, line drawings, etc.).
9. Video
Video listings are simply search results that offer videos. These will crop up in SERPs whenever Google judges it relevant to the search query.
10.Top Stories
Top Stories are specifically news-related results that appear at the top of a SERP. These are only served up by Google if there are any current events or ongoing news items related to the search query.
11. Twitter
Twitter informational cards display the most recent or trending tweets related to the search query typed into Google’s search bar. These tend to appear around halfway down the SERP.
12. Shopping Ads
Although not technically SERP features (they are actually paid advertisements) Shopping Ads are an inescapable, ubiquitous part of the SERP feature landscape. Shopping Ads are displayed in response to queries for specific products, and show up in results as product ads placed by businesses using the Google Shopping network.
13. Google Ads
Like shopping ads, Google Ads are not organic SERP Features. But these paid advertisements always win the SERP wars, which means we can’t leave them off our SERP feature list.
Taking up prime real estate, Google Ads usually take up the first four positions on the SERP. Prime real estate does cost more and it’s worthwhile to remember that not only do you a pay a premium for first result Google Ads, but that positioning is also an indicator of a higher level of competition for a keyword.
Note: While Google Ads usually take prime position at the top of a SERP, they are also sometimes found lurking at the bottom if there are enough advertisers. This is not really an ideal position to be in, especially if you’re paying for it. If you find your paid ads there, it’s time to rethink your PPC strategy and how well it’s working.
What is Search Intent?
Search intent, also referred to as search query intent or keyword intent, is the ultimate goal of the person using a search engine. To find search intent, ask yourself:
“What is the searcher most likely looking for when they type ‘insert keyword/search phrase’ into Google??
What is a Search Intent Modifier?
Often, a user will use what we call a ‘search intent modifier’ to indicate the above mentioned intent – the actual thing they are looking for.
For example, a user may include the word “buy? in their keyword search to indicate they want to make a purchase – say “buy coffee beans?; or they may include the word “best? in their keyword search to indicate they want to compare products/service to find the best one – say “best pizza place?
Some basic types of search engine user intent, with examples of modifiers, include:
1. Informational Intent Based Search
Informational search intent is driven by someone looking to learn about a topic and gain new knowledge, no matter how in depth the topic may be.
Search Intent Modifier examples:
- How to
- What is
- How big
- History of
- Meaning of
2. Commercial Intent Based Search
Commercial search intent is driven by a searcher looking to gain more information before purchasing an item. This could include model types, product reviews, pricing, warranties, brands, and so on.
Search Intent Modifier examples:
- Best
- Compare
- Top
- Reviews
- New
3. Transactional Intent Based Search
Transactional search intent is driven by a searcher ready to make a purchase or commit to an action (ex. Sign up for a newsletter).
Search Modifier Examples:
- Buy
- Coupon
- Free shipping
4. Local Intent Based Search
Local search intent is driven by a searcher looking for something specific to their neighborhood or city.
Search Intent Modifier examples:
- Coffee shops near me
- Takeout pizza close by
- Local plumbers in Vancouver
How SERP Features Respond to Search Intent Modifiers
In 2017, the team at getstat.com recently posted an article titled How SERP Features Respond to Search Intent Modifiers which shows that swapping search intent modifiers can result in dramatic changes to Google SERPs features.
STAT examined the 20 top SERP results (minus organics) for various search modifiers and compiled the numbers into extremely useful percentage points. For the purposes of this article, we have listed the top three types of SERP features based on their percentage in relation to the number of searches analyzed.
(Note: In updating this blog post we could not find another similar current study on how SERP features respond to search intent modifiers in 2020 or 2021. We have left the following information as is, as it is still relevant and useful.)
Search modifiers categorized by search intent were used to search on mobile devices in the US. The results provide some useful data for pursuing intent based search engine marketing and optimization. Let’s have a look.
1. SERP Features Triggered by Informational Search Intent Modifiers
No modifiers were used for informational searches, but the results are still interesting. News results came in a surprising third place, but given that the keyword was found in the article title, this isn’t overwhelmingly unusual.
2. SERP Features Triggered by Commercial Search Intent Modifiers
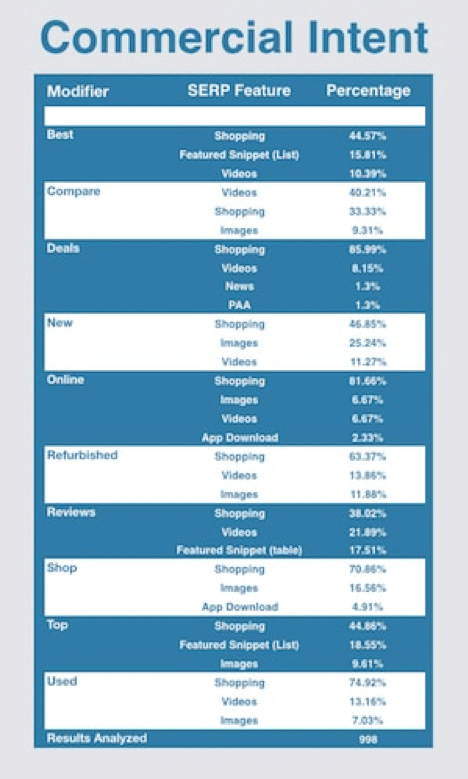
The most common commercial keyword modifiers for search intent purposes are found in the table below. We’ve shown the top 3 features for each modifier to highlight those with the most beneficial payoff.
Shopping Boxes led the entire Commercial intent category with the exception of the Compare modifier. Shopping also has substantial exposure for the modifiers “Deals? at 85.99% and “Used? at 74.92%.
Take note: STAT zeroed in on the potential of Featured Snippets (lists) for keyword modifiers “Best? and “Top? These percentages are comparatively low and either Google is reluctant to present more of them in SERPs or there simply aren’t enough suitable Featured Snippets (lists) to present. This could be a golden opportunity for strategists focusing on such snippets.
3. SERP Features Triggered by Transactional Search Intent Modifiers
The most common transactional modifiers for search intent purposes can be found in the table below. As with the commercial modifiers, we’ve selected the top 3 SERP features found in the results using the modifier to highlight those with the best potential yield.
As STAT indicates, people want to quickly determine how much an item is going to cost – and likely search for the most affordable option. Google seems to feel that Featured Snippets (paragraphs) are an effective way to present this information for the Cost and Price modifiers.
Take note: Images were presented to a significant degree where the Price modifier was concerned. This is somewhat surprising, as one would think at this stage of intent that numbers would supersede images.
4. SERP Features Triggered by Local Search Intent Modifiers
Because STAT only used Chicago and Dallas as local modifiers, there were few results. You can see that Shopping, Places, and Images are the most popular type of SERP Feature.
Take note: We recommend that you perform a variety of searches with local intent for your own city. Search for local businesses, upcoming events, organizations, and so on in your area and see what type of results are shown.

Search Intent Optimization Tips
When it comes to planning modifiers to optimize your SEO for search intent, it really boils down to this key takeaway:
Develop and optimize your site content so that it easily answers users’ questions and/or easily allows them to complete their intended transaction.
Here’s how to do just that for each of the four kinds of search intents identified earlier, followed by more specific details on how to optimize for some of the key (unpaid) SERP features themselves.
1. Informational Intent Optimization
Given that information intent queries tend to ask questions like “what is? and “how to?, the trick to optimizing for informational intent is to first pose the same questions in full, and then answer them – immediately and on the most important, and easily accessible, pages of your site. So, for example, you can pose the question in your page titles and header tags, then answer it in your body copy directly below.
- Create FAQ lists and schema markup around the FAQ section on the page.
- Use “On This Page” type feature to generate Sitelink snippets.
2. Commercial Intent Optimization
Videos, images and featured snippets all stand out in the STAT report as potential goldmines. Use them.
- Add high quality images with appropriate, useful alt-tags;
- Share engaging videos showing exactly what your product/services can do for users;
- Use lists – bulleted or numbered – showcasing your wares, their features, and pros and cons.
All simple but effective ways to optimize for commercial success.
3. Transactional Intent Optimization
The key to optimizing for transactional search intent is to make it fog-horn obvious to the user both how can take that action and convert, and why they should do so.
- Use eye-catching, clear, concise CTAs that leave no room for uncertainty that the user must click this button to complete their search journey.
- Keep the conversion process quick and easy. Limit forms as much as possible, don’t make users dig around from page to page on your site to find all the information necessary to make the final decision, give auto-form-filler as an option.
- Don’t oversell: simplify the decision process for the user, leading them to convert, by offering descriptions of your product or offering that are both truthful and salient.
4. Local Intent Optimization
According to Google, 88% of people who conduct a local search on their smartphone visit a related store within a week.
Local search is big. And important. Luckily it’s also fairly simple to optimize for local search intent.
- Claim and optimize your Google Business Listing. Google’s powerful free platform allows businesses to maintain accurate address and contact information, manage online reviews, promote products and services, and engage with customers.
- Claim and optimized other relevant key listings – Yelp, TripAdvisor, Bing Places, as well as social media channels. They’re not Google, but they all have millions of customers. Plus search engines use them too as a measure of how up to date your information is.
- Make your site mobile friendly. By 2021, mobile devices will influence more than $1.4 trillion in local sales. (Forrester) Did you know that mobile users are 5 times more likely to abandon a task if the website isn’t optimized for mobile?
- Make sure your local contact details – physical address, phone number, parking information etc. is up to date and accurate.
How to Optimize for Specific SERP Features
Featured Snippets
Google can do a lot of crawling for you, but making it easier on them can only win you brownie points – and featured snippet spots. If you want to win a Featured Snippet bulleted list for example, pre-format your content as a bulleted list with the target keyword in a subheading.
Pro tip: Make sure you fully understand the power of Featured Snippets by reading “How Featured Snippets in Search Can Boost Your Website Traffic? and “How to Avoid Eliminated Featured Snippets?
If you are going to go this route, check out these current How To articles for the current best practices:
- Moz.com: How to Optimize for Google’s Featured Snippets
- Ahrefs.com: How to Optimize for Google’s Featured Snippets
- SearchEngineLand.com: Featured Snippets: The 9 Rules of Optimization
- SEMRush.com: How to Optimize for Google Featured Snippets [Research]
Local Pack
As per optimizing for local intent, make sure your Google Business listing is claimed and up to date. Same goes for all your social media channels and other important listings like Yelp.
You should also check out Google’s current Improve your local ranking on Google support page.
Instant Answer / Knowledge Graph
Given that the Instant Answer SERP feature is sourced from Google’s Knowledge Graph (another SERP feature), the key to optimizing for Instant Answer lies in optimizing for Knowledge Graph. Google pulls data for this from all over the web, which means making sure your information and content is up to date and relevant to current times is key. Your About Us page, your Google Business listing, any Wikipedia pages which may exist about you, Yelp, Facebook… basically, if your name or brand appears anywhere on the web, you need to make sure the information that goes with it is right.
Here are some current How To optimize for quick answers box articles you’ll want to check out before starting:
- SearchEngineLand.com: Optimizing for the Google Quick Answers Box
- SearchEngineJournal.com: Optimize Your Site for Google Answer Box
People Also Ask (PAA)
Start by looking at your pages that rank for the most keywords. Pick one of these pages and gather all the ranking keywords. From here, you can use a tool like SEMRush to grab all the PAA questions for the keywords. Decide which questions make the most sense to optimize for based on your website’s purpose, visitor’s intent and the question’s popularity. From here, write a good answer.
By adding more context and in-depth content for key search terms to your pages, Google has more to work with and is more likely to include you in their PAA drop downs.
Here are some current resources for optimizing PAA:
- SEMRush.com: How to Optimize for People Also Ask
- Moz.com: People Also Ask: 5 Key Facts & How to Optimize for PAA
- SearchEngineWatch.com: How to Make the Most of Google’s “People Also Ask? results
Reviews
The first step is to get your customers to write reviews and for you to interact with all reviews (both good and bad). The next step is to make sure that you website has the proper schema markup to be eligible to show review snippets in SERPs.
To get the full skinny on reviews – their importance for SEO, how to optimize them, how to deal with them, and why you need them – read “How Customer Reviews Can Impact Your SEO? Short on time? Know this: Google has stated that “high-quality, positive reviews from your customers will improve your business’s visibility and increase the likelihood that a potential customer will visit your location.? In short: get reviews, respond to reviews.
Sitelinks
Google will auto-generate sitelinks whenever they think it relevant and useful to the user. But they can only do so if they can easily find them. Make sure your site structure is easily and logically navigable site, with unique page-level metadata.
Images
Google still relies on words to fully crawl the images on your website. For all current images on your website and new images being added, make sure that they:
- Have a descriptive file name
- Have human readable URLs
- Descriptive, useful alt tags
- Captions
- Used alongside relevant copy/content
Google (and your users) also can’t bear a slow-loading image, so make sure your images are sized and optimized for web. All of this will make your images, and ultimately your site, more likely to pop up in the image SERP feature.
Knowledge Panel
Google only pulls information for the Knowledge Panel from Google Business and Google Maps. If you’ve done as we’ve told you and optimized for Local Search/Local Pack, you don’t need to worry about optimizing for Knowledge Panel.
Benefits of Search Intent Targeting
By now it should be clear that optimizing for search intent and specific SERP features, using modifiers, can play a key role in your SEO success. By delivering content optimized for this to Google, you allow Google to deliver more relevant search results to users. This, in turn, allows Google to deliver your site back to those users – in any number of formats.
Done right, this kind of targeting means that you will see more traffic, more qualified traffic, and ultimately, more converted traffic to your site – the trifecta of traffic as we like to call it. And all thanks to paying attention to one or two extra words.
General FAQs About Search Intent
What is search intent?
Search intent (or search query intent or keyword intent) is the motive behind any given Internet search. It is the ultimate goal of what the searcher is most likely searching for when typing in their keyword search into Google.
What is a search intent modifier?
An intent modifier is a word/words that signal the intent behind any search query. For example, the modifier ‘buy’ signals a person is looking to make a purchase, ‘near me’ signals a person is looking for something specific to an area, and ‘best’ signals the person is looking to compare items before making a purchase.
What is keyword intent?
Keyword intent is the intention behind a persons’ search. There are three primary intents: Navigational (want to reach a particular website), Information (gain information), and Transactional (perform a specific task – such as make a purchase).
How do I find search intent?
You can usually determine search intent based on a query report, such as the Google Search Console Query Report. The wording of the query typically tells you what the person is looking for. Once you find search intent make sure that your corresponding website pages match this intent and give the searcher what they want.
For more information about Advanced SEO Techniques such as search intent marketing and optimization please contact 1st on the List today by calling 1-877-563-0459 or email us at [email protected].
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published on August 21, 2019 and has been completely revamped and updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness.

